Researchers can create customized organs for people maybe quite soon.
When we want to create lots of biomaterials. By using biotechnology, we must find out what we want to create. If we want to make lots of spider webs, that is one of the hardest materials in nature. We can make hybrid cells for that thing. If we want to connect the genome that makes spider make its silk to the cell that makes animal fur. And that thing makes those cells create spider silk. In some other versions, the genome that makes the spider's silk will connect with the cotton.
That allows vegetables to make that extremely hard material. So these kinds of things are making biotechnology interesting. Nanotechnology allows creating the synthetic DNA. And that thing makes it possible to create the vegetables there is electric eel's genomes. Those bioelectric batteries can revolutionize technology. And also, the DNA transplant allows the creation of cloned neurons for half-organic microchips.
Researchers also created mini-lungs in the laboratory. Those lungs can use in infection research. But the same technology can use to create cloned lungs for humans. If in those cells is connected a gene that makes them grow very fast. That kind of technology allows the creation of transplant organs for people. In that model, the organs are made by cloning the receiver's cells. But the problem is how to make them grow faster than normal cells.
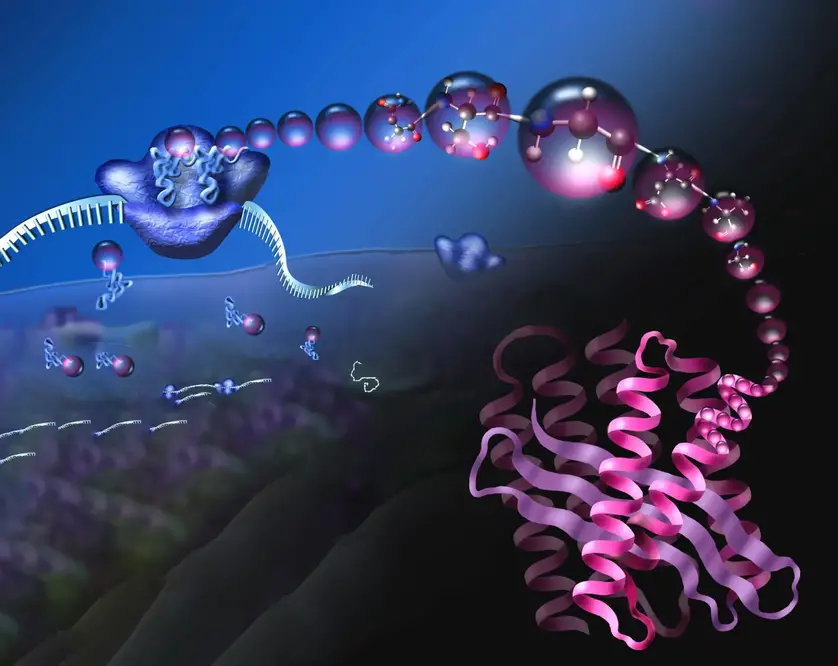
"Ribosomes (blue, upper left) are nanomachines that read mRNA (coming in from left) to assemble a chain of amino acids (magenta balls) that folds into a compact 3D protein (lower right, pink). Credit: Adapted from NSF image." (ScitechDaily.com/Hijacking Cellular Factories: Retooling the Ribosomal Translation Machine to Biosynthesize Molecules)
Researchers created the first synthetic human embryo in a laboratory.
The synthetic human is one of the most fascinating things in science fiction. In some models, synthetic humans can make interstellar trips, and they can act as special forces operators. And of course, synthetic human embryos can use in medical tests. There is always the possibility that some worker in those laboratories wants a baby very hard. And in that case, that kind of person can steal one of those embryos. In that case that synthetic humans must treat as others. Synthetic human embryos are always causing discussions.
Hybridization of humans and other species is possible. There are tests where the human embryo is hybridized with mice, and that thing hoped to create cloned organs for medical tests. But by using that technology is possible to create perfect organ transplants for people simply by cloning their organs. And that thing is one of the most interesting things in the world. In some visions, the genome that makes bowhead whales immune to cancer can connect with human genomes. And also things that make Greenland shark very long living can connect with human genomes.
Genome therapy is one of the newest therapies. In that therapy, the genome transplants would fix genetic disorders. But there is the possibility that gene therapy can use to create new immune cells like modified B- lymphocytes that can create medicines that destroy cancer cells. Genetically engineered immune cells can also change the DNA in the cell's nucleus.
There is the possibility that the cells will get a genome transplant where they form new stem cells in the human body. In that model, every person's stem cell DNA will be stored after their birth. If researchers can make that thing and those genomes can store in liquid nitrogen they guarantee that every person can get stem cells from the cloned cells that grow in cell cultures.
Hijacking cellular factories in the human body can program the cells to produce something that person is missing. Those cells can produce things like cytostatics. The genetically engineered immune cells that can create fibrine or spider web can use to fix the damage in blood veins. Those cells can also make it possible to close blood veins that transport nutrients for the tumors. Or they can close damaged blood veins in the case of accidents.
Those genetically engineered cells can also create baby cells that are different from those cells. The genetically engineered macrophage can create bone cells as the next-generation cells. That will make it possible to fix damaged bones. There is the possibility that microchip-controlled genetically engineered macrophages can remove non-wanted cells from the human body.
https://www.theguardian.com/science/2023/jun/14/synthetic-human-embryos-created-in-groundbreaking-advance
https://scitechdaily.com/how-to-guide-for-creating-mouse-human-chimeric-embryos/
https://scitechdaily.com/lab-grown-mini-lungs-accelerating-respiratory-disease-research/
https://scitechdaily.com/hijacking-cellular-factories-retooling-the-ribosomal-translation-machine-to-biosynthesize-molecules/


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.