Samples are ready to deliver from Mars o Earth. But before, no samples are taken to the laboratory. We must realize one thing. There is the rocket that must send to Mars. Then that sample must take to the rocket's cargo bay. After that, the rocket must launch its engines. And the rocket requires fuel and oxygen. There are two possible versions of the rocket that NASA and ESA can use in that mission.
The rocket can fill its tanks on Mars by benefiting water that is on that planet's surface. The system splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen by using electrolysis. And other rocket version uses fuel that is stored in the rocket. That system is in use for nuclear missiles.
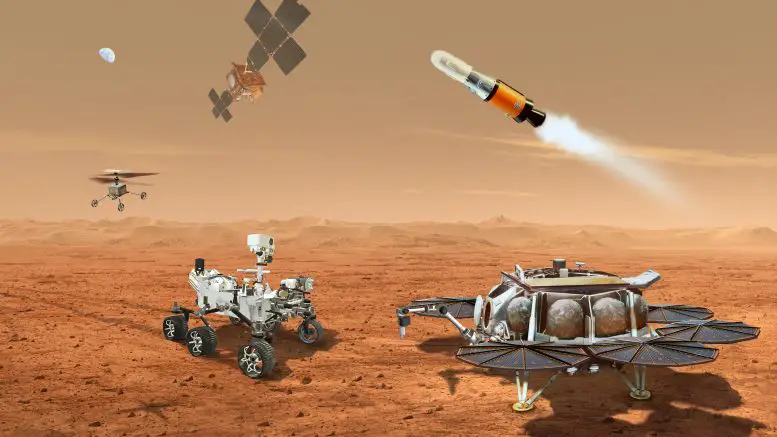
"This illustration shows a concept for multiple robots that would team up to ferry to Earth samples collected from the Mars surface by NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech". (ScitechDaily.com/Mission Impossible? NASA Calls in Expert Panel to Review Mars Sample Return Plans)
NASA calls an expert panel to discuss and review the return plans of Mars samples. Theoretically, there is knowledge about how to handle rockets that should bring samples from the red planet. And how to take samples from the planet Mars to Earth? The problem is that if something goes wrong with the rocket that mission must start again. The rocket can use water on Mars's surface as an energy source. The electrolytic system can break water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen.
That system requires that there is enough water on the planet, that the system can send a rocket back to Earth. Another possibility is to send the rocket, where oxygen and fuel are stored in the stages into Mars, as I wrote before. And that thing doesn't require fuel and oxygen production on Mars. The system can use similar technology to Space X's multi-use rockets that can launch and land vertically.
So could an unmanned version of Space X's Starship shuttle be the first craft that pics samples from Mars and brings them to Earth? In that case, the samples can position two rockets to minimize the effects of the spacecraft's destruction. Then we must realize one thing. If the chamber where those samples are stored will be damaged. That means those samples will be polluted.
To eliminate the possibility that all samples will be polluted the system might analyze part of those samples in orbiting trajectory or on the Moon. In that case, the laboratory can install on board the Starship spacecraft. If some organic material affects those samples before they are in the laboratory. That thing destroys the mission to find Martian bacteria fossils from those stones.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.